SVN used for configuration management
Like every UNIX server admin, I’m using many various text based configurations on my machines. It’s important to track “every” change of these important files to prevent problems with service stability.
I decided to set up Subversion server and store all useful configurations from my Linux boxes there. For this purpose I wrote script svnci which is used to save/delete/update files from svn. You can off course save all necessary files to SVN by hand, but it’s quicker to write short parser for it.
The idea is to create main repository “system_configs” where you will have subdirectories correspond to hostnames of your machines:
└── system_configs
├── debian
└── czbrn0208
Then the access rights are set for each host to access the right directory in SVN. Then you should be able to commit changes to SVN using svn+ssh and private keys.
Use cron to automatically check changes in your files and add them to SVN.
Here is the example how I installed subversion server to debian and managed configuration files in it.
SVN server installation and configuration together with WebSVN
Install necessary software:
Prepare SVN directory:
mkdir /home/svn
mkdir /home/svn/.ssh
mkdir /var/lib/svn-repos
chown -R svn:svn /home/svn
svnadmin create --fs-type fsfs /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs
Now it’s necessary to setup access rights for servers which will read/write configuration to your SVN server. In my example I will use servers with hostnames “debian” and “czbrn0208″.
[/czbrn0208]
czbrn0208 = rw
[/debian]
debian = rw
EOF
[general]
authz-db = authz
anon-access = none
EOF
Now you have to create directory structure matching the hostnames and import it to SVN:
svn import /tmp/repo file:///var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs -m "Initial import (`date +\"%F %T\"`)"
rm -rf /tmp/repo
We should also change rights to “svn” user:
chown -R svn:svn /var/lib/svn-repos
You should check your SVN directory structure and it should look like:
/
debian/
czbrn0208/
Now you need to add public keys to: /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys to allow access from hosts to SVN server using svn+ssh.
I include here also ssh key generation:
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
e4:e7:b9:75:10:97:e4:4b:28:2d:ad:69:65:d2:3d:78 root@debian
The key's randomart image is:
+--[ RSA 2048]----+
| . |
| + * . |
| . + X E |
| o O = o |
| S = . . |
| + . . |
| o . . |
| o . |
| . |
+-----------------+
Now you should save $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub to /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys like:
--tunnel-user=`hostname`\",no-port-forwarding,no-pty,no-agent-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding \
`cat $HOME/.ssh/id_rsa.pub`" >> /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys
I should do the same for my second host czbrn0208, but I have to first transfer it’s public key to the server and then run similar command:
--tunnel-user=czbrn0208\",no-port-forwarding,no-pty,no-agent-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding \
`ssh root@czbrn0208 "cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"`" >> /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys
root@debian:/ cat /home/svn/.ssh/authorized_keys
command="/usr/bin/svnserve -t -r /var/lib/svn-repos --tunnel-user=debian",no-port-forwarding,no-pty,no-agent-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA7INCS6YC4VtsBpPa7H3sg4grSeRXSosWhWFzqyNDf++pau37DH1wZYCunfBpJjbiVMFJnOoT3LPmNc7DUTipEUAbz8p9XNt20qG8edLuf2zJ1VrqCxTydIJon+X+ZT6CI95v6/xG3SBevRKaV07kwzxIPdLMhJKdF0d7HKUOGTgWrWGIoRCnxSyIO5Jn7qEA+7/h7IYZo94IOedwDi1009akOfU73Iw/ArxtDAM752UNf7Y0gANtJRngBdT1nkiW1Yko2OPMG+gMDkc4bZ14TYqXzHeFHSGD/ipZlKn9czry3z5Pw5quI/K6m6uaWP9WuMC/CEjhRmNbOpsVRNg00Q== root@debian
command="/usr/bin/svnserve -t -r /var/lib/svn-repos/system_configs --tunnel-user=czbrn0208",no-port-forwarding,no-pty,no-agent-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAABIwAAAQEA4p/ax75qZ5KiI1j3uy3rmgNFjyaxflKdVN0mQKPg4xzHAIy2cVdAk9eVdmNJOCKzjJej4dEL2NwgR0LDaaVJelZt2tI/GMZj4VnxLyAJQeJEeyMuUccwDJLF4X6CtUP22f7dzkHe6ovpRgBdUiuNWlmmOVkTwJqgQMp6P7c5BtKA60VLWvu1dfnChbJ8hay+9y890n893egOm6aAHpzbsaSPF0DxqrkNnVYrabOh4Y7HoXuKwJNdQtbR0zKdnURTk+GWMiUgyMU5NkEAC9GqAzVN/t+4NWZHDWuS1VlBdNbt1pmfMNhlUAIm/tsWtPdPwYEnI8MqolQHnHSDw9KYeQ== root@czbrn0208
root@debian:/
Now you should be able to access SVN from the hosts:
root@debian:/ svn co svn+ssh://svn@debian.xvx.cz/`hostname` /root/configuration-`hostname`
root@czbrn0208:~ mkdir /root/configuration-`hostname`
root@czbrn0208:~ svn co svn+ssh://svn@debian.xvx.cz/`hostname` /root/configuration-`hostname`
Now your repositories are ready to import first files/directories:
svn add /root/configuration-debian/rc.local
svn ci --message "Test" /root/configuration-debian/
Now there should be first file in the repository.
Now you can access your repository by WebSVN using http://my_server/websvn.
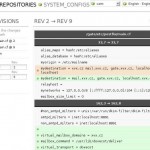
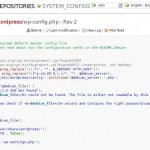
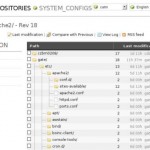
Everybody like screenshots so I put there some from my own SVN server:
snvci script
Here is a link for my script which can help you to add/update/remove to svn repository without deep knowledge of it: http://websvn.xvx.cz/wsvn-websvn.xvx.cz/projects/trunk/scripts/svnci/svnci.
I use it because it’s faster and easy to remember than learn various svn commands combined with shell – so here are some examples:
Add files to repository:
`/etc/freeradius/sql.conf' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sql.conf'
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sql.conf
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sql.conf
Sending root/configuration-gate/files
Transmitting file data ..
Committed revision 36.
Initial: /etc/freeradius/sql.conf
gate:/# svnci /etc/freeradius/sites-available/default
/etc/freeradius/sites-available -> /root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available
`/etc/freeradius/sites-available/default' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available/default'
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available/default
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/freeradius/sites-available/default
Sending root/configuration-gate/files
Transmitting file data ..
Committed revision 37.
Initial: /etc/freeradius/sites-available/default
Add directory to repository:
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 2010-02-25 17:02 cron.monthly
gate:/etc# svnci cron.monthly
/etc/cron.monthly -> /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly
`/etc/cron.monthly/.placeholder' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/.placeholder'
`/etc/cron.monthly/debsums' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums'
`/etc/cron.monthly/standard' -> `/root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard'
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/.placeholder
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums
A /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/.placeholder
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums
Adding root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard
Sending root/configuration-gate/files
Transmitting file data ....
Committed revision 38.
Initial: /etc/cron.monthly/
Removing file(s):
gate:/etc/cron.monthly# svnci -r debsums standard
Removing /etc/cron.monthly/debsums from repository: D /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums
Removing /etc/cron.monthly/standard from repository: D /root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard
Deleting root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/debsums
Deleting root/configuration-gate/etc/cron.monthly/standard
Sending root/configuration-gate/files
Transmitting file data .
Committed revision 39.
For updating files included in your repository you can use “svnci -u” command. It’s also handy to run it every night by cron to automatically track changes in your “monitored” files:
Sending configuration-gate/etc/apache2/httpd.conf
Sending configuration-gate/etc/apache2/sites-available/default-ssl
Sending configuration-gate/etc/munin/plugin-conf.d/munin-node
Sending configuration-gate/packages
Sending configuration-gate/root/bin/files
Transmitting file data .............
Committed revision 45.
Useful links:
http://jimmyg.org/blog/2007/subversion-over-svnssh-on-debian.html

Tak a look at this tool http://sourceforge.net/projects/pmsvn
Peter,
This looks good, but how are you updating your configuration files on the servers? ln -s?
We are kicking around this idea as well, but we are going a different route with it.
Grouping all of our machines based on type. so we will have:
/reporoot
/Linux
/Solaris
/AIX
/…
I would much rather update three files, instead of 250.
Hello Dave.
I’m updating the configurations by script using cron every midnight.
In this article I just wanted to show what are the possibilities of having config files in SVN repository, because it’s good idea (according me). You can easily track the changes on the machines.
I agree it can be handy to have machines grouped by OS type. I prefer to keep configs per hosts – because if something is not working well on the box I can see all it’s changes.
But it’s just my preference….
I’m sure everybody can script these svn commits/updates and create it’s own solution – here I describe the way how I did it…
See you and good luck…
PetrR